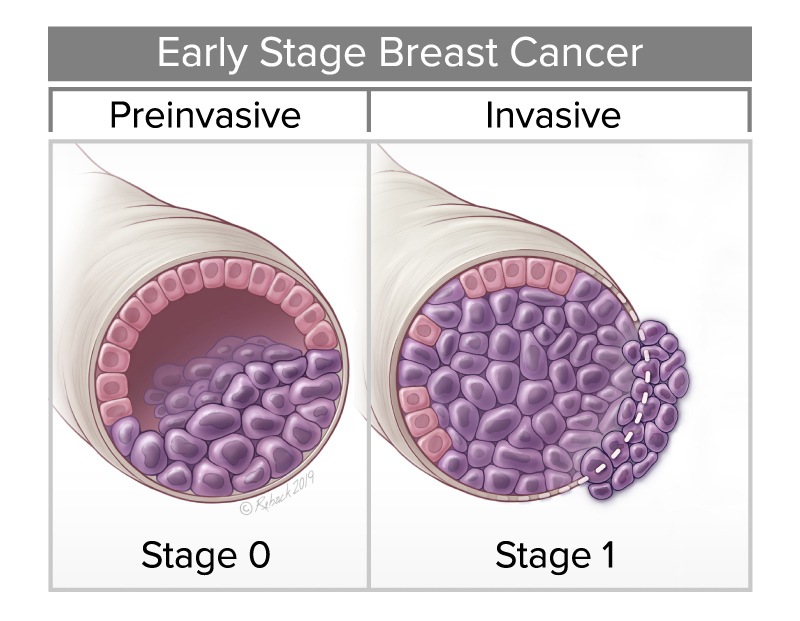
DCIS (Stage 0 Breast Cancer)
What You Should Know
What is DCIS?
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is the presence of abnormal cells inside a milk duct in one of both breasts. DCIS is considered noninvasive and is the earliest form of breast cancer and is sometimes referred to as Stage 0 (zero).
See how DCISionRT can provide you and your doctor helpful information to guide your radiation treatment decisions.
References:
1 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute. (2015). Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer. Retrieved from https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html
2Hwang S. Estimating the magnitude of clinical benefit of local therapy in patients with DCIS. The Breast. 2019;44. doi:10.1016/s0960-9776(19)30073-6.
3American Cancer Society. (2019). Mastectomy. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/treatment/surgery-for-breast-cancer/mastectomy.html
4Susan G. Komen. (2020). Side Effects of Radiation Therapy. Retrieved from https://ww5.komen.org/BreastCancer/SideEffectsofRadiationTherapy.html
5Susan G. Komen. (2020). Side Effects of Tamoxifen. Retrieved from https://ww5.komen.org/BreastCancer/SideEffectsofTamoxifen.html
6Miller M, et al. Contralateral Breast Cancer Risk in Women with Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: Is it High Enough to Justify Bilateral Mastectomy? Annals of Surgical Oncology. 2017;24(10):2889-2897. doi:10.1245/s10434-017-5931-2.
7Overview of the Randomized Trials of Radiotherapy in Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast. by EBCTCG JNCI Monographs. 2010;2010(41):162-177. doi:10.1093/jncimonographs/lgq039.
8Cuzick J, et al. Eect of tamoxifen and radiotherapy in women with locally excised ductal carcinoma in situ: long-term results from the UK/ANZ DCIS trial. The Lancet Oncology. 2011;12(1):21-29. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(10)70266-7.
9Timbrell S, et al. Comparison of Local Recurrence After Simple and Skin-Sparing Mastectomy Performed in Patients with Ductal Carcinoma In Situ. Annals of Surgical Oncology. 2016;24(4):1071-1076. doi:10.1245/s10434-016-5673-6.
10Breastcancer.org. (2019). Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Retrieved from https://www.breastcancer.org/symptoms/types/dcis#:~:text=According%20to%20the%20American%20Cancer,are%20living%20much%20longer%20lives
11Petridis, C., Brook, M.N., Shah, V. et al. Genetic predisposition to ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Breast Cancer Res 18, 22 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-016-0675-7.
12Mayo Clinic. (2020). Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS). Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/dcis/symptoms-causes/syc-20371889.